WPF之XAML基础
文章目录
- XAML基础:深入理解WPF和UWP应用开发的核心语言
- 1. XAML简介
- XAML与XML的关系
- 2. XAML语法基础
- 元素语法
- 属性语法
- 集合语法
- 附加属性
- 3. XAML命名空间
- 命名空间映射关系
- 4. XAML标记扩展
- 静态资源引用
- 数据绑定
- 相对资源引用
- 常见标记扩展对比
- 5. XAML与代码的关系
- XAML部分:
- C#代码隐藏部分:
- XAML编译过程
- 6. 依赖属性系统
- 依赖属性定义示例
- 依赖属性特性
- 7. 资源系统
- 资源字典
- 资源查找范围
- 8. XAML中的数据绑定基础
- 基本绑定语法
- 绑定到对象属性
- 绑定模式
- 9. 样式和模板基础
- 样式
- 触发器
- 10. 实际应用示例
- MainWindow.xaml:
- MainWindow.xaml.cs:
- 11. XAML调试技巧
- Visual Studio中的XAML调试工具
- 启用绑定调试
- x:Name与x:Key的区别
- 12. XAML最佳实践
- 结构组织
- 性能考虑
- 可维护性
- 测试和兼容性
- 总结
- 学习资源
XAML基础:深入理解WPF和UWP应用开发的核心语言
1. XAML简介
XAML (eXtensible Application Markup Language,可扩展应用程序标记语言) 是由微软开发的一种基于XML的标记语言,最初用于WPF (Windows Presentation Foundation) 应用程序的UI设计。如今,XAML已成为多个微软技术的基础,包括WPF、UWP (Universal Windows Platform)、Xamarin.Forms和.NET MAUI等。
XAML将用户界面元素与业务逻辑分离,采用声明式方法定义UI,从而使开发人员和设计人员能够更有效地协作。通过XAML,我们可以清晰地描述应用程序的视觉层,而不需要编写大量的过程代码。
XAML与XML的关系
XAML是XML的一种特定应用形式,因此它遵循所有XML语法规则:
- 必须有一个根元素
- 元素必须正确嵌套
- 标签区分大小写
- 所有元素必须关闭
- 属性值必须使用引号
2. XAML语法基础
元素语法
XAML中的每个UI元素都通过XML标签表示,对应于.NET类型系统中的类:
<Button Content="点击我" />
上面这段XAML代码创建了一个Button控件实例,并设置其Content属性为"点击我"。
属性语法
XAML支持两种设置属性的方式:
- 使用XML属性语法:
<Button Content="点击我" Width="100" Height="30" />
- 使用属性元素语法(特别适用于复杂的属性值):
<Button Width="100" Height="30"><Button.Content><StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"><Image Source="icon.png" Width="16" Height="16" /><TextBlock Text="点击我" Margin="5,0,0,0" /></StackPanel></Button.Content>
</Button>
集合语法
XAML使用直观的语法处理集合,特别是控件中的子元素:
<StackPanel><Button Content="按钮1" /><Button Content="按钮2" /><TextBox Text="输入文本" />
</StackPanel>
上面的代码在StackPanel中添加了三个子控件,这些控件会被自动添加到StackPanel的Children集合中。
附加属性
XAML的一个重要特性是附加属性,它允许父元素设置子元素的特性:
<Grid><Button Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="2" Content="网格中的按钮" />
</Grid>
这里的Grid.Row和Grid.Column是由Grid控件定义的附加属性,它们应用在按钮上以指定按钮在网格中的位置。
3. XAML命名空间
XAML使用XML命名空间来组织和引用不同类库中的类型。WPF应用程序中常见的XAML命名空间包括:
<Window xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"xmlns:local="clr-namespace:MyApplication"x:Class="MyApplication.MainWindow"Title="XAML示例" Height="350" Width="500"><!-- 窗口内容 --></Window>
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"- 默认命名空间,包含核心WPF控件xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"- XAML语言定义命名空间,包含x:Class等XAML特定属性xmlns:local="clr-namespace:MyApplication"- 引用当前应用程序中定义的类型
命名空间映射关系
4. XAML标记扩展
XAML标记扩展提供了一种强大的方式来扩展基本XAML语法。它们使用花括号语法 {ExtensionName Parameter}:
静态资源引用
<Button Background="{StaticResource MyBrush}" Content="使用资源" />
数据绑定
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Username}" />
相对资源引用
<TextBlock Text="{RelativeSource FindAncestor, AncestorType={x:Type Window}, Path=Title}" />
常见标记扩展对比
| 标记扩展 | 用途 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| StaticResource | 引用静态定义的资源 | {StaticResource MyBrush} |
| DynamicResource | 引用可能在运行时改变的资源 | {DynamicResource ThemeColor} |
| Binding | 数据绑定 | {Binding Path=Name} |
| TemplateBinding | 模板内部的绑定 | {TemplateBinding Foreground} |
| x:Static | 引用静态字段或属性 | {x:Static SystemColors.HighlightBrush} |
| x:Null | 表示空值 | {x:Null} |
5. XAML与代码的关系
在WPF应用程序中,XAML文件通常与代码隐藏文件(.xaml.cs)成对出现。它们之间通过部分类机制关联:
XAML部分:
<Window x:Class="XamlDemo.MainWindow"xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"Title="XAML演示" Height="350" Width="500"><Grid><Button x:Name="myButton" Content="点击我" Click="myButton_Click" Width="100" Height="30" /></Grid>
</Window>
C#代码隐藏部分:
using System.Windows;namespace XamlDemo
{public partial class MainWindow : Window{public MainWindow(){InitializeComponent();}private void myButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e){MessageBox.Show("按钮被点击了!");}}
}
XAML编译过程
在编译过程中,XAML被转换为BAML (Binary Application Markup Language),然后作为资源嵌入到程序集中。在运行时,这些BAML资源被加载并重构为UI对象树。
6. 依赖属性系统
XAML与WPF的依赖属性系统紧密相关。依赖属性扩展了传统的.NET属性,提供属性值继承、动画支持、样式应用等功能。
依赖属性定义示例
public class MyControl : Control
{public static readonly DependencyProperty IsActiveProperty =DependencyProperty.Register("IsActive", typeof(bool), typeof(MyControl),new PropertyMetadata(false, OnIsActiveChanged));public bool IsActive{get { return (bool)GetValue(IsActiveProperty); }set { SetValue(IsActiveProperty, value); }}private static void OnIsActiveChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e){MyControl control = (MyControl)d;bool newValue = (bool)e.NewValue;// 处理属性变化}
}
依赖属性特性
- 属性值继承
- 变更通知
- 支持动画
- 支持样式和模板
- 支持数据绑定
7. 资源系统
XAML资源系统允许定义和重用各种UI元素,如颜色、样式、模板等。
资源字典
<Window.Resources><SolidColorBrush x:Key="PrimaryBrush" Color="#FF3333" /><Style x:Key="ButtonStyle" TargetType="Button"><Setter Property="Background" Value="{StaticResource PrimaryBrush}" /><Setter Property="Foreground" Value="White" /><Setter Property="Padding" Value="10,5" /></Style>
</Window.Resources><StackPanel><Button Content="样式按钮" Style="{StaticResource ButtonStyle}" /><TextBlock Text="红色文本" Foreground="{StaticResource PrimaryBrush}" />
</StackPanel>
资源查找范围
资源查找按照上述层次结构,从最特定的范围开始向上查找。
8. XAML中的数据绑定基础
XAML数据绑定是连接UI和数据的桥梁,使界面能够自动反映数据变化。
基本绑定语法
<TextBox x:Name="nameInput" Width="200" />
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Text, ElementName=nameInput}" Margin="0,10,0,0" />
上面的代码将TextBlock的Text属性绑定到nameInput控件的Text属性。
绑定到对象属性
// 视图模型类
public class PersonViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{private string _name;public string Name{get { return _name; }set{if (_name != value){_name = value;OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Name));}}}public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;protected void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName){PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));}
}
<!-- XAML中设置DataContext并绑定 -->
<StackPanel><TextBox Text="{Binding Name, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /><TextBlock Text="{Binding Name}" Margin="0,10,0,0" />
</StackPanel>
// 在代码中设置DataContext
public MainWindow()
{InitializeComponent();DataContext = new PersonViewModel { Name = "John Doe" };
}
绑定模式
XAML支持多种绑定模式:
| 绑定模式 | 描述 | 场景 |
|---|---|---|
| OneWay | 从源到目标的单向绑定 | 显示数据但不需要回写 |
| TwoWay | 双向绑定,数据可以双向流动 | 编辑表单数据 |
| OneTime | 初始化时绑定一次,之后不更新 | 静态数据显示 |
| OneWayToSource | 从目标到源的单向绑定 | 特殊场景数据收集 |
9. 样式和模板基础
XAML样式和模板系统允许彻底自定义UI外观,同时保持逻辑与表现分离。
样式
<Window.Resources><Style x:Key="RoundedButton" TargetType="Button"><Setter Property="Background" Value="#FF3333" /><Setter Property="Foreground" Value="White" /><Setter Property="Padding" Value="10,5" /><Setter Property="Template"><Setter.Value><ControlTemplate TargetType="Button"><Border Background="{TemplateBinding Background}"CornerRadius="15"Padding="{TemplateBinding Padding}"><ContentPresenter HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" /></Border></ControlTemplate></Setter.Value></Setter></Style>
</Window.Resources><Button Content="圆角按钮" Style="{StaticResource RoundedButton}" />
触发器
触发器可以根据属性值改变或事件发生来改变元素外观:
<Style x:Key="HighlightButton" TargetType="Button"><Setter Property="Background" Value="DarkBlue" /><Setter Property="Foreground" Value="White" /><Style.Triggers><Trigger Property="IsMouseOver" Value="True"><Setter Property="Background" Value="RoyalBlue" /><Setter Property="Foreground" Value="Yellow" /></Trigger><Trigger Property="IsPressed" Value="True"><Setter Property="Background" Value="Navy" /></Trigger></Style.Triggers>
</Style>
10. 实际应用示例
下面是一个简单但完整的WPF应用程序示例,展示了XAML的多种功能:
MainWindow.xaml:
<Window x:Class="XamlDemo.MainWindow"xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"xmlns:local="clr-namespace:XamlDemo"Title="联系人应用" Height="450" Width="500"><Window.Resources><SolidColorBrush x:Key="PrimaryColor" Color="#2196F3" /><SolidColorBrush x:Key="AccentColor" Color="#FF4081" /><Style x:Key="HeaderText" TargetType="TextBlock"><Setter Property="FontSize" Value="20" /><Setter Property="FontWeight" Value="Bold" /><Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,0,0,20" /><Setter Property="Foreground" Value="{StaticResource PrimaryColor}" /></Style><Style TargetType="Button"><Setter Property="Background" Value="{StaticResource PrimaryColor}" /><Setter Property="Foreground" Value="White" /><Setter Property="Padding" Value="15,5" /><Setter Property="Margin" Value="0,5" /><Style.Triggers><Trigger Property="IsMouseOver" Value="True"><Setter Property="Background" Value="{StaticResource AccentColor}" /></Trigger></Style.Triggers></Style></Window.Resources><Grid Margin="20"><Grid.RowDefinitions><RowDefinition Height="Auto" /><RowDefinition Height="*" /></Grid.RowDefinitions><TextBlock Text="联系人管理系统" Style="{StaticResource HeaderText}" /><Grid Grid.Row="1"><Grid.ColumnDefinitions><ColumnDefinition Width="*" /><ColumnDefinition Width="250" /></Grid.ColumnDefinitions><!-- 联系人列表 --><ListBox x:Name="contactList" ItemsSource="{Binding Contacts}" SelectedItem="{Binding SelectedContact}" Margin="0,0,20,0"><ListBox.ItemTemplate><DataTemplate><StackPanel Margin="5"><TextBlock Text="{Binding Name}" FontWeight="Bold" /><TextBlock Text="{Binding Email}" FontSize="11" /></StackPanel></DataTemplate></ListBox.ItemTemplate></ListBox><!-- 联系人详情 --><StackPanel Grid.Column="1" DataContext="{Binding SelectedContact}"><TextBlock Text="联系人详情" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,0,0,10" /><TextBlock Text="姓名" Margin="0,5,0,0" /><TextBox Text="{Binding Name, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /><TextBlock Text="邮箱" Margin="0,5,0,0" /><TextBox Text="{Binding Email, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /><TextBlock Text="电话" Margin="0,5,0,0" /><TextBox Text="{Binding Phone, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /><TextBlock Text="地址" Margin="0,5,0,0" /><TextBox Text="{Binding Address, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" AcceptsReturn="True" TextWrapping="Wrap" Height="60" /><StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="0,15,0,0"><Button Content="添加新联系人" Command="{Binding DataContext.AddCommand, RelativeSource={RelativeSource FindAncestor, AncestorType={x:Type Grid}}}" /><Button Content="删除联系人" Command="{Binding DataContext.DeleteCommand, RelativeSource={RelativeSource FindAncestor, AncestorType={x:Type Grid}}}"Margin="10,5,0,5" /></StackPanel></StackPanel></Grid></Grid>
</Window>
MainWindow.xaml.cs:
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Input;namespace XamlDemo
{public partial class MainWindow : Window{public MainWindow(){InitializeComponent();DataContext = new ContactViewModel();}}public class ContactViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged{private Contact _selectedContact;public ObservableCollection<Contact> Contacts { get; } = new ObservableCollection<Contact>();public Contact SelectedContact{get { return _selectedContact; }set{_selectedContact = value;OnPropertyChanged(nameof(SelectedContact));}}public ICommand AddCommand { get; }public ICommand DeleteCommand { get; }public ContactViewModel(){// 添加示例数据Contacts.Add(new Contact { Name = "张三", Email = "zhangsan@example.com", Phone = "138-0000-0001", Address = "北京市海淀区" });Contacts.Add(new Contact { Name = "李四", Email = "lisi@example.com", Phone = "139-0000-0002", Address = "上海市浦东新区" });SelectedContact = Contacts[0];AddCommand = new RelayCommand(_ =>{var newContact = new Contact { Name = "新联系人" };Contacts.Add(newContact);SelectedContact = newContact;});DeleteCommand = new RelayCommand(_ =>{if (SelectedContact != null){Contacts.Remove(SelectedContact);SelectedContact = Contacts.Count > 0 ? Contacts[0] : null;}}, _ => SelectedContact != null);}public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;protected void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName){PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));}}public class Contact : INotifyPropertyChanged{private string _name;private string _email;private string _phone;private string _address;public string Name{get { return _name; }set{if (_name != value){_name = value;OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Name));}}}public string Email{get { return _email; }set{if (_email != value){_email = value;OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Email));}}}public string Phone{get { return _phone; }set{if (_phone != value){_phone = value;OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Phone));}}}public string Address{get { return _address; }set{if (_address != value){_address = value;OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Address));}}}public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;protected void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName){PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));}}public class RelayCommand : ICommand{private readonly Action<object> _execute;private readonly Predicate<object> _canExecute;public RelayCommand(Action<object> execute, Predicate<object> canExecute = null){_execute = execute ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(execute));_canExecute = canExecute;}public bool CanExecute(object parameter){return _canExecute == null || _canExecute(parameter);}public void Execute(object parameter){_execute(parameter);}public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged{add { CommandManager.RequerySuggested += value; }remove { CommandManager.RequerySuggested -= value; }}}
}
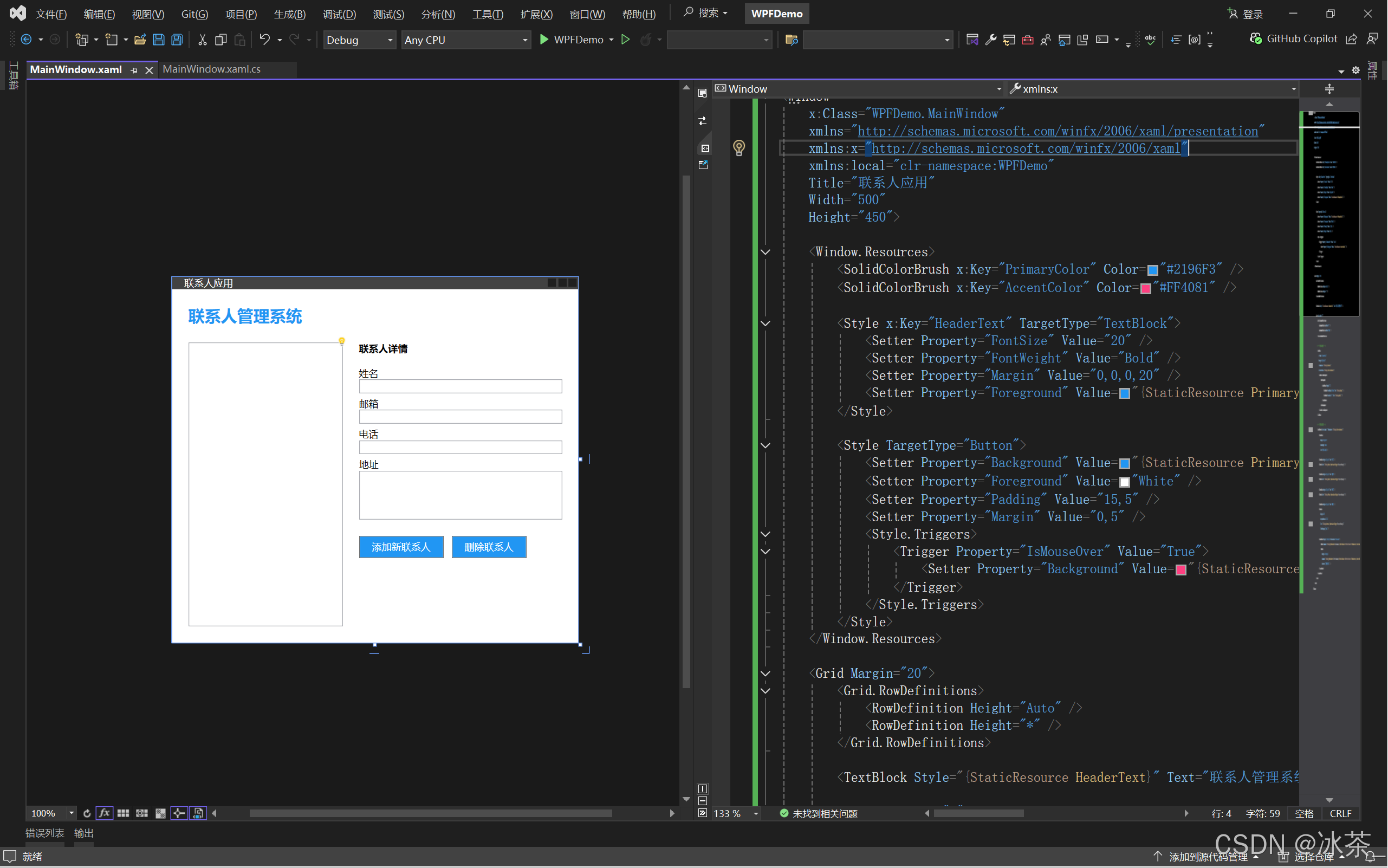
此应用程序界面演示了XAML中的多种功能:
- 资源和样式
- 数据绑定
- 命令绑定
- 数据模板
- 布局控制
- 相对源绑定
- 触发器
11. XAML调试技巧
调试XAML可能具有挑战性,以下是一些有用的技巧:
Visual Studio中的XAML调试工具
- 实时可视化树:在运行时查看应用程序的视觉树结构
- 绑定调试:使用TraceSource在输出窗口中显示绑定错误
- 热重载:在运行时修改XAML并立即查看效果(最新版VS支持)
启用绑定调试
// 在App.xaml.cs的构造函数中添加
public App()
{// 启用绑定调试PresentationTraceSources.DataBindingSource.Switch.Level = SourceLevels.Warning;
}
x:Name与x:Key的区别
| 特性 | x:Name | x:Key |
|---|---|---|
| 用途 | 在代码中引用元素 | 在资源字典中标识资源 |
| 访问方式 | 直接访问命名元素 | 通过资源查找 |
| 生成成员 | 生成代码隐藏中的字段 | 不生成代码成员 |
| 适用场景 | 控件、页面元素 | 样式、模板、画刷等资源 |
12. XAML最佳实践
结构组织
- 使用逻辑分层结构组织XAML
- 使用资源字典分离样式与布局
- 为复杂UI创建用户控件
性能考虑
- 避免深层嵌套布局
- 适当使用虚拟化
- 控制绑定更新频率
- 使用缓存静态资源
可维护性
- 保持表现与逻辑分离
- 为复杂属性使用属性元素语法
- 使用适当的命名约定
- 添加注释说明复杂区域
测试和兼容性
- 在不同分辨率下测试
- 考虑国际化需求
- 验证高对比度主题下的表现
- 确保键盘可访问性
总结
XAML是一种强大而灵活的UI描述语言,它允许开发人员和设计师以声明式方式创建复杂的用户界面。通过本文,我们了解了XAML的基础语法、依赖属性系统、资源管理、数据绑定和样式模板等核心概念。掌握XAML是成为优秀WPF或UWP开发者的关键一步。
随着.NET技术的发展,XAML的重要性持续增长,它已经扩展到多个平台和框架中。深入理解XAML将帮助你更有效地构建富客户端应用程序,并为探索更高级的技术(如MVVM架构模式)奠定基础。
学习资源
以下是一些深入学习XAML的优质资源:
- Microsoft官方WPF文档
- XAML概述(微软官方文档)
- WPF Tutorial
- XAML 2009规范
- Pro WPF in C# 2010(书籍)
- XAML在Stackoverflow上的问答
- WPF Sample Applications
- Microsoft Learn - WPF学习路径
无论你是初学者还是有经验的开发人员,持续实践和探索是掌握XAML的最佳方式。创建小型项目,尝试不同的控件和布局,分析现有应用程序的XAML代码,这些都将帮助你更深入地理解和应用XAML技术。
