playwright 实现自动上传,多元素操作
1. 文件上传
在Playwright中,使用locator.setInputFiles()完成文件上传操作。
单个文件
await page.getByLabel('Upload file')
.setInputFiles(path.join(__dirname, 'myfile.pdf'));多个文件
await page.getByLabel('Upload files')
.setInputFiles([
path.join(__dirname, 'file1.txt'),
path.join(__dirname, 'file2.txt'),
]);清除文件
传入空数组即可
await page.getByLabel('Upload file')
.setInputFiles([]);内存缓存
// Upload buffer from memory
await page.getByLabel('Upload file').setInputFiles({
name: 'file.txt',
mimeType: 'text/plain',
buffer: Buffer.from('this is test')
});2. 事件监听page.on('filechooser')
文件上传通常实现类似于
<input type="file">..如果不是类似上面的动态创建方式的话,就需要监听对应event:
// Start waiting for file chooser before clicking. Note no await.
const fileChooserPromise = page.waitForEvent('filechooser');
await page.getByLabel('Upload file').click();
const fileChooser = await fileChooserPromise;
await fileChooser.setFiles(path.join(__dirname, 'myfile.pdf'));3. 完整示例
3.1 Playwright项目配置
以NodeJS为例,配置如下 确保你的项目已经配置好Playwright。如果还没有,可以使用以下命令安装Playwright:
npm install playwright3.2 编写上传自动化测试
import { test, expect }from'@playwright/test';
import*as path from'path';
// 文件路径
const filePath = path.resolve(__dirname,'tests/fixtures/demo.zip');
// 具体的测试用例
test('文件上传自动化测试', async ({ page })=>{
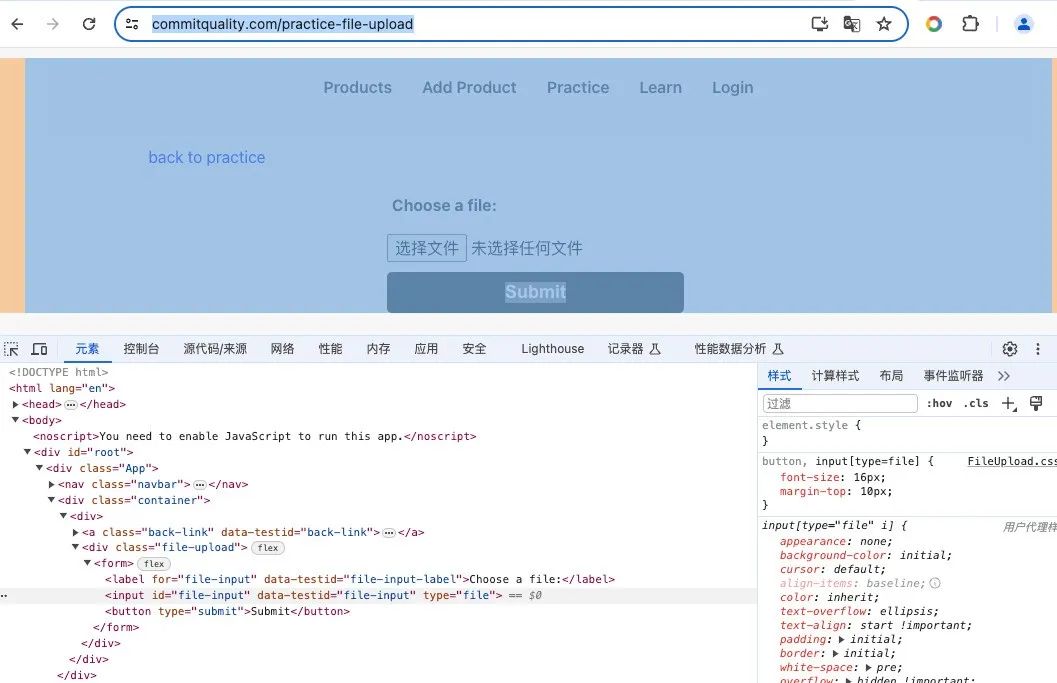
// 打开目标页面
await page.goto('https://commitquality.com/practice-file-upload');
// 找到文件输入元素
const inputFile = await page.locator('input[type="file"]');
// 上传文件
await inputFile.setInputFiles(filePath);
// 验证文件是否上传成功
await expect(page.locator('text=demo.zip')).toBeVisible();
});
小结论
文件自动化上传在Playwright中是比较容易容易的,主要是调用.setInputFiles()方式实现,从而轻松实现自动化文件上传的交互操作。
多元素操作
在自动化测试中,操作和验证多个元素是常见的需求。Playwright 提供了丰富的API方法来操作和验证页面上的多个元素,包括 .all(), .count(), .first(), .last(), .nth(), .toHaveCount() 等
4. 介绍
Playwright是一个功能强大的自动化测试库,支持跨浏览器测试。它不仅可以操作单个元素,还提供了多种方法来操作和验证多个元素。这些方法使测试代码更加简洁和易读,同时提高了测试的可维护性。
5. 相关方法详解
5.1 .locator()API
.locator()支持如下定位策略,返回匹配成功的元素,可能包含多个:
css
const button = page.locator('button.submit');xPath
const listItem = page.locator('//ul/li[3]');ID
const passwordField = page.locator('#password');text
const heading = page.locator('text="Welcome!"');组合
const loginButton = page.locator('text="Login" >> css=button');5.2 .getBy()系列
.getByText()
page.getByText('world');.getByAltText()
await page.getByAltText('Playwright logo').click();.getByRole()
await page.getByRole('checkbox', { name: 'Subscribe' }).check();.getByLable()
await page.getByLabel('Username').fill('john');.getByPlaceHolder()
await page
.getByPlaceholder('name@example.com')
.fill('playwright@microsoft.com');.getByTitle()
await expect(page.getByTitle('Issues count')).toHaveText('25 issues');.getByTestId()
await page.getByTestId('directions').click();5.3 .and()和.or()组合
.and()
// .and组合
const button = page.getByRole('button').and(page.getByTitle('Subscribe'));
expect(button).toHaveCount(1); // 断言数量.or()
//.or组合
const newEmail = page.getByRole('button', { name: 'New' });
const dialog = page.getByText('Confirm');
await expect(newEmail.or(dialog)).toBeVisible();5.4 多元素选择
以下一组api,针对定位结果中的多元素进行操作,包括个数计算、选择某元素,断言个数等。
.all()
.all() 方法返回一个包含所有匹配元素的数组。
for (const li of await page.getByRole('listitem').all())
await li.click();.count()
.count() 方法返回匹配元素的数量。
const count = await page.locator('selector').count();
constole.log(count);.first()
.first() 方法返回第一个匹配元素。对于文本类定位,一般文本类型,加上这个会更不易出错。
await page.locator('搜索').first().click;.last()
.last() 方法返回最后一个匹配元素。
await page.locator('搜索').last().click;.nth()
.nth(index)方法返回指定索引的匹配元素(索引从 0 开始)。
const banana = await page.getByRole('listitem').nth(2);.toHaveCount()
.toHaveCount(count)方法用于断言匹配元素的数量。
const list = page.locator('list > .component');
await expect(list).toHaveCount(3);5.5 多元素操作
.click():点击
await locator('#id').click();.fill():填充内容
await locator('#box').fill('text');.textCount():获取文本
const text = await locator('#id').textContent();.toBeVisible(): 可见性
await expect(locator).toBeVisible();6. 实战示例
以下是一个综合示例,展示了如何在实际测试中使用这些方法:
import { test, expect }from'@playwright/test';
test('comprehensive example', async ({ page })=>{
await page.goto('https://example.com');
// 获取所有匹配元素
const allElements = await page.locator('selector').all();
console.log(`Total elements: ${allElements.length}`);
// 获取元素数量
const count = await page.locator('selector').count();
console.log(`Element count: ${count}`);
// 操作第一个元素
await page.locator('selector').first().click();
// 操作最后一个元素
await page.locator('selector').last().click();
// 操作第三个元素(索引从 0 开始)
await page.locator('selector').nth(2).click();
// 断言元素数量
await expect(page.locator('selector')).toHaveCount(3);
});结论
在自动化测试中,操作和验证多个元素是不可避免的任务。Playwright 提供的 .all(), .count(), .first(), .last(), .nth(), .toHaveCount() 等方法,使得这些操作更加简洁和高效,让你在自动化测试项目中,提高测试的稳定性和可维护性。
