C++ Primer Plus 章节编程题练习 1-9章包含题目,答案以及知识点总结
第3章


3.1
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "string"
#include<Windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
const int unit = 12;
int height;
cout << "请输入身高(英寸)__:";
cin >> height;
int inch = height * unit;
cout << height << "英寸转换成英尺是 : " << inch << endl;
return 0;
}
3.2
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "string"
#include<Windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
const double yingChi_to_yingCun = 12;
const double yingCun_to_M = 0.0254;
const double Bang_to_kg = 1.0/2.2;
double yingChi;
cout << "请输入身高(英尺)__:";
cin >> yingChi;
double Bang;
cout << "请输入体重(榜)__:";
cin >> Bang;
double BMI = Bang * Bang_to_kg / sqrt(yingChi * yingChi_to_yingCun * yingCun_to_M);
cout << "身高为" << yingChi << "英尺," <<"体重为" << Bang <<"的人的BMI是" << BMI <<endl;
return 0;
}
3.3
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "string"
#include<Windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
const double degree_to_minute = 60;
const double minute_to_second = 60;
double degree;
double minute;
double second;
cout << "Enter a latituede in degree, minites, adn second:" << endl;
cout << "Fisrt, enter the degrees:";
cin >> degree;
cout << "Next, enter the minutes:";
cin >> minute;
cout << "Finally, enter the second:";
cin >> second;
double result = degree + second * (1 / minute_to_second) * (1 / degree_to_minute) +
minute * (1 / degree_to_minute);
cout << degree << " degrees, " << minute << " minutes, " << second << " seconds = " << result;
return 0;
}

3.4
- 版本1
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "string"
#include<Windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
const double day_to_hour = 24;
const double hour_to_minute = 60;
const double minute_to_second = 60;
long InputSeconds ;
cout << "Enter the number of seconds:";
cin >> InputSeconds;
double days, hours, minites, seconds;
days = InputSeconds * (1 / minute_to_second) * (1 / hour_to_minute) * (1 / day_to_hour);
hours = (days - int(days)) * day_to_hour;
minites = (hours - int(hours)) * hour_to_minute;
seconds = (minites - int(minites)) * minute_to_second;
cout << InputSeconds << " seconds = " << int(days) << " days, "
<< int(hours) << " hours,"
<< int(minites) << " minites,"
<< seconds << " seconds" << endl;
return 0;
}
- 版本2
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
#include "string"
#include<Windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
const long day_to_hour = 24;
const long hour_to_minute = 60;
const long minute_to_second = 60;
long InputSeconds;
cout << "Enter the number of seconds:";
cin >> InputSeconds;
long days, hours, minites, seconds;
long totalMinute, totalHour;
seconds = InputSeconds % minute_to_second;
totalMinute = InputSeconds / minute_to_second; //总秒数转成分
minites = totalMinute % minute_to_second;
totalHour = totalMinute / hour_to_minute; //总分数转成小时
hours = totalHour % hour_to_minute;
days = totalHour/day_to_hour;
cout << InputSeconds << " seconds = " << days << " days, "
<< hours << " hours,"
<< minites << " minites,"
<< seconds << " seconds" << endl;
return 0;
}

3.5 注意,不是long long int
int main(void) {
long long global, America;
//global = 6898758899;
//America = 310783781;
cout << "Enter the world's population:";
cin >> global;
cout << "Enter the America's population:";
cin >> America;
double result = 100.0 * America / global;
cout << "百分比: " << result << "%";
return 0;
}
第4章



4.1 string 使用getline和cin获取用户输入用法的区别
- 知识点1:输入字符串时,如果定义的是
string类型,可以有两种输入方式,getline(cin, FirtName);或者直接cin >> lastName;,前者允许用户输入空格,后者不允许输入空格,如果输入空格,空格后面的字符串将不会被读取 - 知识点2:字母转换,直接可以
char(grade + 1),添加强制类型转换即可
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
string FirtName, lastName;
cout << "fisrt name:";
getline(cin, FirtName);
cout << "lastName name:";
cin >> lastName;
char grade;
cout << "the grade you deserve?";
cin >> grade;
int age;
cout << "age?";
cin >> age;
cout << "Name : " << lastName << " " << FirtName << endl;
cout << "Grade : " << char(grade + 1) << endl;
cout << "Age : " << age << endl;
return 0;
}
4.2 string 使用getline和cin获取用户输入用法的区别 2
int main(void) {
string name;
string dessert;
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
getline(cin, name);
cout << "Enter your dessert:\n";
getline(cin, dessert);
cout << "I have some " << dessert << " for you, " << name;
return 0;
}
4.3 char的用法,strlen获取char长度,strcpy_s复制char字符串,strcat_s字符串拼接
- 知识点1:在使用char数组来放置字符串的时候,如果要一开始就指定char数组的长度,传入的数据必须也只能是
const修饰的常数,const int length = 64;,不加const程序报错;且如果不是const修饰的常数创建指定长度的数组会报错,以下几种方式都不可以
报错
char Name[strlen(Ming) + strlen(Xing) + 1];
报错
const int newLenth = strlen(Ming) + strlen(Xing) + 3;
char Name[newLenth];
- 知识点2:综上所述,如果用变量要创建指定长度的数组,只能用指针,
char* Name = new char[newLenth];,最后记得销毁内存delete[] Name;
int main(void) {
const int length = 64;
char Ming[length],Xing[length];
cout << "Enter your first name:";
cin.getline(Ming, length);
cout << "Enter your last name:";
cin.getline(Xing, length);
int newLenth = strlen(Ming) + strlen(Xing) + 3;
char* Name = new char[newLenth];
strcpy_s(Name, newLenth, Ming);
strcat_s(Name, newLenth, ", ");
strcat_s(Name, newLenth, Xing);
cout << Name;
delete[] Name;
return 0;
}
4.4
int main(void) {
string First_name, last_name;
cout << "Enter your first name:";
cin >> First_name;
cout << "Enter your last name:";
cin >> last_name;
cout << last_name + ", " + First_name;
return 0;
}
4.5
struct CandyBar {
string brand;
double weight;
int kaluli;
};
int main(void) {
CandyBar snack = { "Mocha Munch",2.3,350 };
cout << "snack.brand:" << snack.brand <<
",snack.weight : " << snack.weight << ",snack.kaluli: " << snack.kaluli;
return 0;
}
4.6
struct CandyBar {
string brand;
double weight;
int kaluli;
};
int main(void) {
CandyBar snack;
snack.brand = "Monno";
snack.weight = 2.3;
snack.kaluli = 350;
cout << "snack.brand:" << snack.brand << endl;
cout << "snack.weight : " << snack.weight << endl;
cout << ",snack.kaluli: " << snack.kaluli << endl;
return 0;
}
4.7 普通结构体定义与访问
struct PiSa {
string brand;
double weight;
int diameter;
};
int
main(void) {
PiSa pisa;
cout << "snack.brand:";
getline(cin, pisa.brand);
cout << "snack.weight:";
cin>> pisa.weight;
cout << "snack.diameter:";
cin >> pisa.diameter;
cout << "snack.brand:" << pisa.brand << endl;
cout << "snack.weight : " << pisa.weight << endl;
cout << ",snack.diameter: " << pisa.diameter << endl;
return 0;
}
4.8 结构体指针,结构体使用new来分派空间 PiSa *pisa = new PiSa;,访问用->,记得删除内存delete pisa; pisa= NULL;
struct PiSa {
string brand;
double weight;
int diameter;
};
int main(void) {
PiSa *pisa = new PiSa;
cout << "snack.brand:";
getline(cin, pisa->brand);
cout << "snack.weight:";
cin>> pisa->weight;
cout << "snack.diameter:";
cin >> pisa->diameter;
cout << "snack.brand:" << pisa->brand << endl;
cout << "snack.weight : " << pisa->weight << endl;
cout << ",snack.diameter: " << pisa->diameter << endl;
delete pisa;
pisa= NULL;
return 0;
}
4.9 用指针创建结构体数组 CandyBar *snack = new CandyBar[num];,记得删除内存 delete[] snack; snack = NULL;
struct CandyBar {
string brand;
double weight;
int kaluli;
};
int main(void) {
const int num = 3;
CandyBar *snack = new CandyBar[num];
snack[0].brand = "Monno";
snack[0].weight = 2.3;
snack[0].kaluli = 350;
snack[1].brand = "Monno2";
snack[1].weight = 3.3;
snack[1].kaluli = 450;
snack[2].brand = "Monno3";
snack[2].weight = 4.3;
snack[2].kaluli = 550;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
cout << "snack.brand:" << snack[i].brand << endl;
cout << "snack.weight : " << snack[i].weight << endl;
cout << ",snack.kaluli: " << snack[i].kaluli << endl;
}
delete[] snack;
snack = NULL;
return 0;
}
4.10 array容器的用法,容器初始化array <double, num> arr;

int main(void) {
const int num = 3;
double grade = 0;
array <double, num> arr;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
cout << "第" << i+1 << "次输入";
cin >> arr[i];
grade += arr[i];
}
grade = grade / num;
cout << "平均成绩: " << grade;
return 0;
}
第五章



5.1
int main()
{
int a, b;
cout << "enter a:";
cin >> a;
cout << "enter b:";
cin >> b;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = a; i <= b; i++) {
sum += i;
}
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
5.2 array容器的用法


#include <array>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const int size = 16;
array<long double, size> factorials;
factorials[1] = factorials[0] = 1LL;
for (int i = 2; i < size; i++) {
factorials[i] = i * factorials[i - 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << i << "! = " << factorials[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
5.3
int main()
{
int number, sum = 0;
while (1) {
cout << "enter a number:";
cin >> number;
sum += number;
if (number == 0) {
cout << " sum = " << sum;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
5.4
int main()
{
const double Daphane_CunKuan = 100;
const double Cleo_CunKuan = 100;
const double Daphane_profit = 0.1;
const double Cleo_profit = 0.05;
double Daphane_in = 0, Cleo_in = 0;
int year = 0;
while (1) {
year++;
cout << "year : " << year << endl;
Daphane_in += Daphane_CunKuan * Daphane_profit;
Cleo_in += (Cleo_CunKuan + Cleo_in) * Cleo_profit;
if (Daphane_in < Cleo_in) {
cout << "year : " << year << endl;
cout << "Daphane_in :" << Daphane_in << endl;
cout << "Cleo_in :" << Cleo_in << endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
5.5
int main()
{
const int monthNum = 12;
const string Months[] = { "1月","2月","3月","4月","5月","6月","7月","8月","9月" ,"10月","11月","12月" };
int saleArray[monthNum] = {0};
int saleNum = 0;
for(int i =0 ; i < monthNum; i++){
cout << "enter " + Months[i] + "销售额: ";
cin >> saleNum;
saleArray[i] = saleNum;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < monthNum; i++) {
sum += saleArray[i];
}
cout <<"销售额: " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
5.6
int main()
{
const int monthNum = 3, yearNum = 3;
const string Months[] = { "1月","2月","3月"};
const string Years[] = { "第1年","第2年","第3年" };
int saleArray[monthNum][yearNum] = { 0 };
int saleNum = 0;
for (int j_year = 0; j_year < yearNum; j_year++) {
for (int i_mon = 0; i_mon < monthNum; i_mon++) {
cout << "enter " + Years[j_year] + "," + Months[i_mon] + "销售额: ";
cin >> saleNum;
saleArray[i_mon][j_year] = saleNum;
}
}
int Total = 0;
for (int j_year = 0; j_year < yearNum; j_year++) {
int temp = 0;
for (int i_mon = 0; i_mon < monthNum; i_mon++) {
temp += saleArray[i_mon][j_year];
}
Total += temp;
cout << Years[j_year] + "总销售额: " << temp << endl;
}
cout << "3总销售额: " << Total << endl;
return 0;
}
5.7 交替输入字符串和数字,输入字符串后面,需要添加语句cin.get();,否则将无法输入字符串
错误
正确

#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
using namespace std;
struct Car {
string brand;
int year;
};
int main()
{
int carNum = 0;
cout << "how many car: ";
cin >> carNum;
cin.get();
Car* cars = new Car[carNum];
for (int i = 0; i < carNum; i++) {
cout << "Car #" + to_string(i+1) << endl;
cout << "enter brand:";
getline(cin, cars[i].brand);
cout << "enter year:";
cin>> cars[i].year;
cin.get();
}
delete[] cars;
cars = NULL;
return 0;
}
5.8 strcmp比较char字符串是否相等
int main()
{
const char* endWord = "done";
char word[20];
int wordCount = 0;
cout << "enter word:";
do{
cin >> word;
wordCount++;
} while(strcmp(word, endWord));
cout << "you entered " << wordCount << "word";
return 0;
}
5.8 持续输入, 在输入过程,判断字串是否相等, !=比较string字符串是否相等
int main()
{
const string endWord = "done";
string word;
int wordCount = 0;
cout << "enter word:";
do{
cin >> word;
wordCount++;
} while(word != endWord);
cout << "you entered " << wordCount << "word";
return 0;
}
5.9
5.9.1非数组方式
const char point = '.';
const char xing = '*';
int num;
cout << "endter row:";
cin >> num;
for (int row = 1; row <= num; row++) {
for (int p = 0; p < num-row; p++) {
cout << point;
}
for (int x = 0; x < row; x++) {
cout << xing;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
5.9.2 一维指针数组存二维char数据,动态分配char数组内存
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const char point = '.';
const char xing = '*';
int num;
cout << "endter row:";
cin >> num;
char* array = new char[num*num];
int p, row, x;
for ( row = 1; row <= num; row++) {
for ( p = 0; p < num-row; p++) {
array[(row - 1) * num + p] = point;
// cout << (row - 1) * num + p;
cout << point;
}
for ( x = 0; x < row; x++) {
array[(row - 1) * num + p + x] = xing;
// cout << (row - 1) * num + p + x;
cout << xing;
}
cout << endl;
}
int count =0;
for (int k = 0; k < num * num; k++) {
count++;
cout << array[k];
if (count % num == 0 && k >0) {
cout << endl;
}
}
delete [] array;
array = NULL;
return 0;
}
- 换行的地方可以做如下优化
for (int k = 0; k < num * num; k++) {
cout << array[k];
if ((k+1) % num == 0 && k >0) {
cout << endl;
}
}
- 第二种实现
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::cin;
int
main (void)
{
const char k_ch1 = '.';
const char k_ch2 = '*';
cout << "Enter number of rows: ";
unsigned uRows;
cin >> uRows;
char* pCharLst = new char [uRows * uRows];
for (unsigned i = 0; i < uRows; ++i) {
for (unsigned j = 0; j < uRows-i-1; ++j) {
pCharLst[i*uRows + j] = k_ch1;
}
for (unsigned j = uRows-i-1; j < uRows; ++j) {
pCharLst[i*uRows + j] = k_ch2;
}
}
for (unsigned i = 0; i < uRows*uRows; ++i) {
cout << pCharLst[i];
if (0 == (i+1) % uRows) {
cout << endl;
}
}
delete [] pCharLst;
pCharLst = NULL;
cout << endl;
return (0);
}
5.9.3 二维指针数组存二维数据,动态分配char数组内存
- 知识点:
char** array = new char*[num];定义的是 指针数组,存放的是指针,所以要使用一层循环进行内存的分配
// 为每一行分配num内存
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
array[i] = new char[num];
}
- 释放内存的时候,也需要使用循环进行释放
// 释放内存
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
delete[] array[i]; // 释放每一行的内存
}
delete[] array; // 释放指针数组
int main()
{
const char point = '.';
const char xing = '*';
int num;
cout << "endter row:";
cin >> num;
char** array = new char*[num]; //指针数组
// 为每一行分配num内存
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
array[i] = new char[num];
}
for (int row = 0; row < num; row++) {
for (int p = 0; p < num-row-1; p++) {
array[row][p] = point;
// cout << (row - 1) * num + p;
cout << point;
}
for (int p = num - row-1; p < num; p++) {
array[row][p] = xing;
cout << xing;
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "-------------------" << endl;
for (int row = 0; row < num; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < num; col++) {
cout << array[row][col];
}
cout << endl;
}
// 释放内存
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
delete[] array[i]; // 释放每一行的内存
}
delete[] array; // 释放指针数组
return 0;
}
第六章





6.1 isupper islower tolower toupper 大小写字母转换和判断,持续输入回车显示 while(cin >> in && in != label)
int main()
{
const char label = '@';
char in;
while(cin >> in && in != label){
if (!isdigit(in)) {
if (isupper(in)) {
cout << char(tolower(in));
}else if (islower(in)) {
cout << char(toupper(in));
}
else
{
cout << in;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
6.2 循环输入并读取,遇到非数字结束,while (cin >> in && count < 10) ,由于定义in 已经是double类型了,就不需要判断in是不是数字了,已经默认输入类型必须是数字
int main()
{
double arrDonation[10];
double in, sum =0;
int count = 0;
// while(cin >> in && isdigit(in) && count <10){
while (cin >> in && count < 10) {
arrDonation[count] = in;
sum += in;
++count;
}
sum = sum / count;
cout << "平均值: " << sum << endl;
cout << "大于平均值的数:";
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (arrDonation[i] > sum)
{
cout << arrDonation[i] << " ";
}
}
return 0;
}

6.3
int main()
{
cout << "Please enter one of the following choices :" << endl;
cout << " c) carnivore" << " " << "p) pianst" << endl;
cout << " t) tree" << " " << "g) game" << endl;
const string cWord = "carnivore";
const string pWord = "pianst";
const string tWord = "tree";
const string gWord = "game";
const string str = "A maple is a " ;
char ch;
cout << "Please enter c,p,t,g :";
while(cin >> ch) {
switch (ch) {
case 'c':
cout << str + cWord;
break;
case 'p':
cout << str + pWord;
break;
case 't':
cout << str + tWord;
break;
case 'g':
cout << str + gWord;
break;
default:
cout << endl;
cout << "Please enter c,p,t,g :";
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
6.4 枚举的用法,for循环的等效用法for (const auto& e: lstBops)
- for循环的等效用法: const:表示 e 是只读的,不能在循环中修改。&:表示 e 是引用,避免拷贝元素,提高效率。
for (const auto& e: lstBops) {
cout << e.fullname << endl;
}
等效于:
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
cout << lstBops[i].fullname << endl;
}
- 枚举的用法:默认是整型,从0开始,依次加1;但是也可以指定值,全部指定或者只指定部分


#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
using namespace std;
#define strsize 20
struct Bop {
char fullname[strsize];
char title[strsize];
char bopname[strsize];
int preference;
};
enum PERFERENCE {
TITLE,
BOPNAME,
FULLNAME
};
int main()
{
Bop lstBops[] = { {"Yang Yang", "chinamobile", "yangyang.gnu", TITLE},
{"xiao wang", "microsoft", "xiaowang", BOPNAME},
{"xiao liu", "IBM", "xiaoliu", FULLNAME},
{"xiao zhang", "Huawei", "xiaozhang", TITLE} };
int arraySize = sizeof(lstBops) / sizeof(lstBops[0]);
cout << "arraySize = " << arraySize << endl;
cout << "a.name b.title c.bopname d.preference q.quit" << endl;
cout << "enter your choice : ";
bool label = true;
char ch;
while (cin >> ch && label) {
switch (ch) {
case 'a':
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
cout << lstBops[i].fullname << endl;
}
break;
case 'b':
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
cout << lstBops[i].title << endl;
}
break;
case 'c':
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
cout << lstBops[i].bopname << endl;
}
break;
case 'd':
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
if (lstBops[i].preference == PERFERENCE::TITLE) {
cout << lstBops[i].title << endl;
}
else if (lstBops[i].preference == PERFERENCE::BOPNAME) {
cout << lstBops[i].bopname << endl;
}
else if (lstBops[i].preference == PERFERENCE::FULLNAME) {
cout << lstBops[i].fullname << endl;
}
}
break;
case 'q':
label = false;
cout << "Byb" << endl;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
6.5
int main()
{
double income;
double array[] = { 5000, 15000, 35000 };
double sax = 0;
cout << "enter ";
while (cin >> income && income >0) {
if (income < array[0]) { //5000
sax = 0;
}
else if (income > array[0] && income < array[1]) //5000-15000
{
sax = array[0] * 0 + (income - array[0]) * 0.1;
cout << sax;
}
else if (income > array[1] && income < array[2]) //15000-35000
{
sax = array[0] * 0 + (array[1] - array[0]) * 0.1 + (income - array[1])*0.15;
cout << sax;
}
else if (income > array[2])
{
sax = array[0] * 0 + (array[1] - array[0]) * 0.1 + (array[2] - array[1]) * 0.15 + (income - array[2])*0.2;
cout << sax;
}
}
return 0;
}
- 思路2
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
using namespace std;
#define strsize 20
int main()
{
double income;
double array[4] = { 5000, 10000, 20000,0 };
double sax = 0;
cout << "enter ";
while (cin >> income && income >0) {
if (income < array[0]) { //5000
array[0] = income;
array[1] = array[2] = array[3] = 0;
}
else if (income > array[0] && income < array[1]) //5000-15000
{
array[1] = income - array[0];
array[2] = array[3] = 0;
}
else if (income > array[1] && income < array[2]) //15000-35000
{
array[2] = income - array[1] - array[0];
array[3] = 0;
}
else if (income > array[2])
{
array[3] = income - array[2] - array[1] - array[0];
}
cout << array[0] * 0 + array[1] * 0.1 + array[2] * 0.15 + array[3] * 0.2;
}
return 0;
}
6.6 动态结构体数组 People* peoples = new People[num];
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
using namespace std;
#define strsize 20
struct People {
string name;
double money;
};
int main()
{
const double big_money = 10000;
int num;
cout << "enetr people number: ";
cin >> num;
People* peoples = new People[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
cout << "第" << i << "捐献者:" << endl;
cout << " enter name:"; cin >> peoples[i].name;
cout << " enter money:"; cin >> peoples[i].money;
}
bool have = false;
cout << "Grant Patrons" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (peoples[i].money > big_money) {
cout << peoples[i].name << endl;
have = true;
}
}
if (have == false) {
cout << "none" << endl;
}
cout << "Patrons" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (peoples[i].money < big_money) {
cout << peoples[i].name << endl;
}
}
delete[] peoples;
peoples = nullptr; // 避免悬空指针
return 0;
}
6.7 获取string字符串的第一个字符 char& fisrt = word[0];
- 知识点:
char* first = &word[0]; // 获取第一个字符的地址 char& first = word[0]; // 获取第一个字符的引用char* first = word[0]; 是错误的,因为类型不匹配
int main()
{
string word;
int yuan = 0, fu =0, none =0;
const char Yuan[10] = { 'a','e','i','o','u', 'A','E','I','O','U' };
while (cin >> word && word != "q") {
char& fisrt = word[0];
if (!isalpha(fisrt)) {
none++;
}
else if (1) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (Yuan[i] == fisrt)
{
yuan++;
}
}
}
else
{
fu++;
}
}
cout << yuan << " 元音" << endl;
cout << fu << " 辅音" << endl;
cout << none << " 其他" << endl;
return 0;
}
6.8 读取txt文件,fstream stream("test_(for_linux).txt");,逐字符读取stream.get(ch)
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
fstream stream("test_(for_linux).txt");
unsigned int num = 0;
char ch;
while (stream.get(ch)) {
++num;
}
--num;
cout << "char = " << num;
return 0;
}
6.9 ifs >> num; //ifs >> num 会从文件中读取数据,直到遇到空白字符(空格、换行符或制表符)为止;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
ifs.get(); //读取并丢弃换行符,文件指针移动到下一行的开头。 正确处理了换行符,确保每次读取操作都从正确的位置开始。
getline(ifs, peoples[i].name);
ifs >> peoples[i].money;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
struct People {
string name;
double money;
};
int main()
{
fstream ifs("test_(for_linux).txt");
unsigned num;
ifs >> num; //ifs >> num 会从文件中读取数据,直到遇到空白字符(空格、换行符或制表符)为止
People* peoples = new People[num];
for (unsigned i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
ifs.get(); //读取并丢弃换行符,文件指针移动到下一行的开头。 正确处理了换行符,确保每次读取操作都从正确的位置开始。
getline(ifs, peoples[i].name);
ifs >> peoples[i].money;
}
const double big_money = 10000;
bool have = false;
cout << "Grant Patrons" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (peoples[i].money > big_money) {
cout << peoples[i].name << endl;
have = true;
}
}
if (have == false) {
cout << "none" << endl;
}
cout << "Patrons" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (peoples[i].money < big_money) {
cout << peoples[i].name << endl;
}
}
delete[] peoples;
peoples = nullptr; // 避免悬空指针
return 0;
}
第8章



8.2 结构体引用的使用 void show(const CandBar& candy) {,初始化结构体对象 struct CandBar candy,candy2;,另外const char _brand[]等同于const char* _brand,而string里面提供了赋值运算符重载,使得string类型和char _brand[]可以直接相互赋值
const char _brand[] = "Milleniune Munch", 等式右时常量字符串,左侧需要const修饰才能接- 结构体里面定义的是
string类型,函数里面可以直接const char _brand[] = "Milleniune Munch",最后将char定义的字符串string定义的字符串?const char _brand[]等同于const char* _brand


#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
struct CandBar {
string brand;
double weight;
int hot;
};
void test(CandBar &candy, const char _brand[] = "Milleniune Munch", const double _weight = 2.85, const int _hot = 350) {
candy.brand = _brand;
candy.hot = _hot;
candy.weight = _weight;
}
void show(const CandBar& candy) {
cout << "candy.brand = " << candy.brand << endl;
cout << "candy.hot = " << candy.hot << endl;
cout << "candy.weight = " << candy.weight << endl;
}
int main()
{
struct CandBar candy,candy2;
test(candy);
show(candy);
test(candy2,"jiaozi",2,300);
show(candy2);
return 0;
}
8.3 遍历string类型变量里面的字符 for (auto& s : str),输入允许输入空格 getline(cin, sentence)

string &trans(string &str) {
//isupper islower tolower toupper
for (auto& s : str) {
s = toupper(s);
}
return str;
}
int main()
{
string sentence;
cout << "Enter a string:";
while (1) {
getline(cin, sentence);
if (sentence == "q") {
break;
}
sentence = trans(sentence);
cout << sentence << endl;
cout << "Next string:";
}
return 0;
}
8.4 结构体 或者 指针数组 内存释放方法总结,char*字符串打印 ;结构体里面有指针变量,赋值时需要对结构体变量先分配内存空间,在进行相应的赋值; 函数重载
char testing[] = "Reality isn's what it used to be.";定义的数组,传入函数时,用char *接收,打印时,可以直接打印cout << array << endl;,不需要for循环
void show(const char* array, int times=1) {
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
cout << array << endl;
}
}
strlen计算char *array字符串长度,char *类型字符串拷贝,strcpy_s(stringy.str, stringy.ct + 1, array);- 内存释放
PiSa* pisa = new PiSa;
delete pisa;
pisa = NULL;
CandyBar* snack = new CandyBar[num];
delete[] snack;
snack = NULL;
char* array = new char[num * num];
delete[] array;
array = NULL;
char** array = new char* [num]; //指针数组
// 释放内存
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
delete[] array[i]; // 释放每一行的内存
}
delete[] array; // 释放指针数组

#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
struct Stringy {
char* str; //ponits to a string
int ct; //length of string
};
void set( Stringy& stringy, char *array) {
stringy.ct = strlen(array);
stringy.str = new char[stringy.ct + 1];
strcpy_s(stringy.str, stringy.ct + 1, array); // 复制内容
}
void show(const Stringy & stringy, int times=1) {
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
cout << stringy.str << endl;
cout << stringy.ct << endl;
}
}
void show(const char* array, int times=1) {
for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) {
cout << array << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Stringy beany;
char testing[] = "Reality isn's what it used to be.";
set(beany, testing);
cout << " -------------- show(beany); --------------" << endl;
show(beany);
cout << " -------------- show(beany,2); --------------" << endl;
show(beany, 2);
testing[0] = 'D';
testing[1] = 'u';
cout << " -------------- show(testing); --------------" << endl;
show(testing);
cout << " -------------- show(testing, 3); --------------" << endl;
show(testing, 3);
cout << " -------------- show(Done!) --------------" << endl;
show("Done!");
show(beany);
delete[] beany.str;
beany.str = NULL;
return 0;
}
8.5 函数模板定义template <typename T>,数组作为函数参数传递
- 数组作为函数参数传递:定义一个数组
array[],可以作为函数形参Max(array, len);直接传递,函数原型Max(int array[5], len);
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
T Max(T array[5], int len) {
T maxNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (array[i] > maxNum) {
maxNum = array[i];
}
}
return maxNum;
}
int main()
{
int array[] = { 2, 1, 4, 5, 3 };
int len = 5;
int maxNum = Max(array, len);
cout << "maxNum = " << maxNum << endl;
cout << " -------------------" << endl;
double array2[] = { 2.1, 1.2, 4.4, 5.7, 3.2 };
double maxNum2 = Max(array2, len);
cout << "maxNum = " << maxNum2;
return 0;
}
8.5.1 函数定义 void text(int array[5], int len),在函数里面修改数组的值,main函数里面的值也会相应的改变,但是如果是数,是值传递,函数内修改不会导致函数外的值修改?函数定义里面的数组名,是数组元素的首地址,有地址当然就能就改地址内的值。void text(int *array, int len)和void text(int array[10], int len)是等价的,其他都不改,只将下列程序中的int array[10],修改成int *array,效果完全一样


void text(int array[5], int len) {
cout << "进入函数后打印结果:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
array[0] = 100;
cout << "进入函数,修改值后 打印结果:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int array[] = { 2, 1, 4, 5, 3 };
int len = 5;
cout << "进入函数前打印结果:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
text(array, len);
cout << "函数运行结束后打印结果:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
void swap(int a, int b) {
cout << "进入函数后打印结果: (a,b) = (" <<a << ","<< b << ")" << endl;
int c;
c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
cout << "函数 执行 后打印结果: (a,b) = (" << a << "," << b << ")" << endl;
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
cout << "进入函数前打印结果: (a,b) = (" << a << "," << b << ")" << endl;
swap(a, b);
cout << "函数运行结束后打印结果: (a,b) = (" << a << "," << b << ")" << endl;
return 0;
}
8.6 当作为函数参数时,char array[] 和char *array是等价的,但是当前传入的参数是char*类型的数组,因此函数形参需要修改成char *array[]


#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
char* test(char *array[], int num) {
T test(T array, int num) {
int maxLength = 0;
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
//char target[] = array[i]; //不能直接将一个指针赋值给一个数组,因为数组的大小和内容需要在编译时确定。
char *target = array[i];
int counter = 0;
while (*target ++ != '\0') {
//cout << "*target " << *target;
counter++;
}
if (counter > maxLength) {
maxLength = counter;
pos = i;
}
}
return array[pos];
}
int main()
{
char str1[] = "today";
char str2[] = "is";
char str3[] = "aerretry eer";
char str4[] = "summay";
char str5[] = "today";
char* textArray[5] = { str1,str2,str3,str4,str5 }; //本质是一个char* 类型的指针数组
char *out = test(textArray, 5);
cout << out << endl;
return 0;
}
8.7 函数模板使用指针数组作形参void ShowArray(T *arr[], int n);,函数内获取数组的值*arr[i]
- 原始8.14的代码:
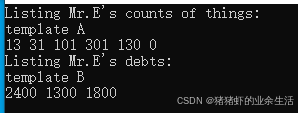
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T >
void ShowArray(T arr[], int n);
template <typename T >
void ShowArray(T *arr[], int n);
struct debts {
char name[50];
double amount;
};
int main()
{
int things[6] = {13,31,101,301.310,130 };
struct debts mr_E[3] = {
{"Ima Wolfe",2400},
{"Ura Foxe",1300.0},
{"Iby Stout",1800.0}
};
double* pd[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
pd[i] = &mr_E[i].amount;
}
cout << "Listing Mr.E's counts of things:\n";
ShowArray(things, 6); // uses template A
cout << "Listing Mr.E's debts:\n";
ShowArray(pd, 3);
return 0;
}
template <typename T >
void ShowArray(T arr[], int n) {
cout << "template A\n";
for (int i= 0; i< n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
template <typename T >
void ShowArray(T* arr[], int n) {
cout << "template B\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << *arr[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
- 按要求改写后
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T >
void ShowArray(T arr[], int n);
template <typename T >
void ShowArray(T *arr[], int n);
template <typename T >
T SumArray(T* arr[], int n);
template <typename T >
T SumArray(T arr[], int n);
struct debts {
char name[50];
double amount;
};
int main()
{
int things[6] = {13,31,101,301,310,130 };
struct debts mr_E[3] = {
{"Ima Wolfe",2400},
{"Ura Foxe",1300.0},
{"Iby Stout",1800.0}
};
double* pd[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
pd[i] = &mr_E[i].amount;
}
cout << "Listing Mr.E's counts of things:\n";
ShowArray(things, 6); // uses template A
cout << "Listing Mr.E's debts:\n";
ShowArray(pd, 3);
double sum1 = SumArray(things, 6);
double sum2 = SumArray(pd, 3);
cout << "sum1 = " << sum1 << endl;
cout << "sum2 = " << sum2 << endl;
return 0;
}
template <typename T >
void ShowArray(T arr[], int n) {
cout << "template A\n";
for (int i= 0; i< n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
template <typename T >
void ShowArray(T* arr[], int n) {
cout << "template B\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << *arr[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
template <typename T >
T SumArray(T* arr[], int n) {
cout << "template C\n";
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += *arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
template <typename T >
T SumArray(T arr[], int n) {
cout << "template D\n";
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum;
}
第七章





7.1 不断循环,一次输入多个数据while (true) {cin >> a >> b; },不是while (cin >> a && cin >> b)
double fun(int a, int b) {
return 2 * a * b / (a + b);
}
int main()
{
int a;
int b;
//while (cin >> a && cin >> b && a != 0 && b != 0) {
// cout << fun(a, b);
//}
while (true) {
cout << "输入一对正整数,计算其调和平均数(0退出):";
cin >> a >> b;
if (0 == a || 0 == b) {
cout << "再会" << endl;
break;
}
cout << " 调和平均数 : " << fun(a, b) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
7.2 传入的是数时,函数形参double gradeArray[]和double *gradeArray等价,此时修改函数里面数组的值,主函数的值也会相应改变
int inputGrade(double gradeArray[], int len) {
int counter = 0;
double grade;
cout << "请输入成绩(输入-1结束)";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << "请输入成绩(输入-1结束):";
cin >> grade;
if (grade == -1) {
break;
}
else {
gradeArray[i] = grade;
counter++;
}
}
return counter;
}
void calGrade(const double *gradeArray, int len) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
sum += gradeArray[i];
}
cout << "平均成绩:" << sum/ len;
}
void showGrade(const double *gradeArray, int len) {
cout << "打印成绩:";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << gradeArray[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
calGrade(gradeArray, len);
}
int main()
{
const int arrayLen = 10;
double gradeArray[arrayLen] = {0};
int len = inputGrade(gradeArray, arrayLen);
showGrade(gradeArray,len);
return 0;
}
7.3 普通结构体定义 struct Box box;或Box box;,函数形参传递结构体值Show(struct Box box)和地址Show(struct Box *box)
struct Box {
char maker[40];
float weight;
float length;
float width;
float volume;
};
void Show(struct Box box) {
cout << " box.weight = " << box.weight << endl;
cout << " box.width = " << box.width << endl;
cout << " box.length = " << box.length << endl;
cout << " box.volume = " << box.volume << endl;
cout << " box.maker = " << box.maker << endl;
}
void Show(struct Box *box) {
box->volume = box->length * box->width * box->weight;
}
int main()
{
struct Box box;
box.weight = 20;
box.width = 10;
box.length = 100;
box.volume = 200;
//box.maker = "chaina";C语言中,数组名是一个常量指针,不能作为左值(即不能直接赋值)。
strcpy_s(box.maker, "China");
Show(box);
cout << "修改后----------" << endl;
Show(&box);
Show(box);
return 0;
}
7.4
double probability(unsigned numbers, unsigned picks);
int main(){
double total, choices;
cout << "Enter the total number of choices on the game card and\n"
"the number of picks allowed:\n";
while ((cin >> total >> choices) && choices < total)
{
cout << "You have one chance in ";
cout << probability(total, choices);
cout << " of winning.\n";
cout << "Next two numbers (q to quit):";
}
cout << " bye\n";
return 0;
}
double probability(unsigned numbers, unsigned picks) {
double result = 1.0;
double n;
unsigned p;
for (n = numbers, p = picks; p > 0; n--, p--) {
result = result * n / p;
}
return result;
}
7.5 递归
int main() {
unsigned int n;
cout << "请输入一个整数(输入负数结束):";
while (cin >> n) {
cout << "n 阶乘是 " << test(n) << endl;
cout << "请输入一个整数(输入负数结束):";
}
}
int test(int n) {
return (n==0)? 1 : n * test(n - 1);
}
7.6 (1) *array数组做为形参,传入后,可直接在函数中当普通数组处理array[counter] = number;;(2)在函数里面定义动态数组,在主函数里面要记得释放内存,delete[] NewArray; // 释放内存; (3)返回数组指针int* Reverse_array(const int *array, int len);,要用指针进行接收,int *NewArray = Reverse_array(array, realLen);

#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
void Show_array(const int *array, const int len);
int Fill_array(int *array, const int len);
int* Reverse_array(const int *array, int len);
int main() {
const int len = 10;
int array[len] = {0};
int realLen = Fill_array(array, len);
cout << "realLen = " << realLen << endl;
Show_array(array, realLen);
int *NewArray = Reverse_array(array, realLen);
cout << "反转后显示" << endl;
Show_array(NewArray, realLen);
delete[] NewArray; // 释放内存
return 0;
}
void Show_array(const int *array, const int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << array[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int Fill_array( int*array, const int len) {
int counter = 0;
int number;
cout << "请输入整数:";
while (cin >> number && counter < len) {
array[counter] = number;
counter++;
cout << "请输入整数:";
}
return counter;
}
int* Reverse_array(const int *array, int len) {
int* newArray = new int [len];
for (int i = 1; i < len - 1; i++) {
newArray[i] = array[len - i - 1];
}
newArray[0] = array[0];
newArray[len-1] = array[len-1];
return newArray;
}
7.7 注意,和数组不同,数组作为函数形参,*array传入的是数组的首地址,在函数内修改数组的值,相应的在函数外的值也会被修改,也就是说此时传入的是地址本身,但是如果是当前案例int *p_start只是一个普通的变量,那么传入的是形参,也就是是值传递,函数内修改变量的值,函数外是不会改变的。所以如果调用Show_array函数时,传入的是 Show_array(p_start, p_end);Show_array(p_start, p_end);,那么整个数组的值都会被打印,后面的无效值也会被打印,因为p_start 和p_end 的指向还是一开始的指向。
int* p_start = &array[0];
int* p_end = p_start + len;
int true_len = Fill_array(p_start, p_end);
Show_array(p_start, p_end);

- 正确的打印应该是下面这样

- 知识点:数组名
array本身也是数组的首地址
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
void Show_array(int *p_start, int *p_end);
int Fill_array(int *p_start, int *p_end);
int main() {
const int len = 10;
int array[len] = {0};
int* p_start = &array[0];
int* p_end = p_start + len;
int true_len = Fill_array(p_start, p_end);
Show_array(p_start, p_start+ true_len);
return 0;
}
void Show_array( int *p_start, int* p_end) {
if (p_start == nullptr || p_end == nullptr) {
cerr << "错误:空指针!" << endl;
return;
}
while (p_start < p_end) {
cout << *p_start << " ";
p_start++;
}
cout << endl;
}
int Fill_array(int* p_start, int* p_end) {
int counter =0;
int number;
cout << "请输入整数:";
while (p_start < p_end && cin >> number) {
*p_start = number;
p_start++;
counter++;
cout << "请输入整数:";
}
p_end = p_start;
return counter;
}
7.8 array标准库容器用法;存储数据的数组作为函数形参,*MoneyArray和MoneyArray []是等价的,都是传递数组的地址,在函数内修改数组,函数外的数组也会相应的改变;存储字符串数组定义const char* Snames[] = { "Spring", "Summer", "Fall", "Winter" };,每一个字符串都相当于一个地址
- 知识点1:#### 7.8.1里的
void fill(double *MoneyArray); //传递地址函数使用,函数里面可以直接使用定义的Seasons和char* Snames[]数组,这里定义的相当于全局变量 - 知识点2:结构体中定义数组,并将结构体作为函数参数传递,结构体变量名并不是指向该结构体的地址,需要使用取址运算符&才能获取其地址,址传递
fill(&money);``以及函数定义void fill(struct Money *money),值传递是show(money);对应的函数定义是void show(struct Money money)
const int Seasons = 4;
const char* Snames[] = { "Spring", "Summer", "Fall", "Winter" };


7.8.1
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
// constant data
const int Seasons = 4;
const char* Snames[] = { "Spring", "Summer", "Fall", "Winter" };
void fill(double *MoneyArray); //传递地址
void show(double *MoneyArray); //传递地址
int main() {
double MoneyArray[Seasons] = {};
fill(MoneyArray);
show(MoneyArray);
return 0;
}
//void fill(const char* Snames[], double* MoneyArray, const int Seasons) {
void fill( double* MoneyArray) {
for (int i = 0; i < Seasons; i++) {
cout << "Enter " << Snames[i] << " expenes: ";
cin >> MoneyArray[i];
}
}
//void show(const char* Snames[], double* MoneyArray, const int Seasons) {
void show(double *MoneyArray) {
double total = 0;
cout << "\nEXPENSE\n";
for (int i = 0; i < Seasons; i++) {
cout << Snames[i] << " : $" << MoneyArray[i] << endl;
total += MoneyArray[i];
}
MoneyArray[0] = 1000;
cout << "Total EXPENSE : $ " << total << endl;
}
7.8.2 结构体中定义数组,并将结构体作为函数参数传递,结构体变量名并不是指向该结构体的地址,需要使用取址运算符&才能获取其地址,址传递fill(&money);``以及函数定义void fill(struct Money *money),值传递是show(money);对应的函数定义是void show(struct Money money)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
// constant data
const int Seasons = 4;
const char* Snames[] = { "Spring", "Summer", "Fall", "Winter" };
struct Money {
double MoneyArray[Seasons];
};
void fill(struct Money *money); //传递地址
void show(struct Money money); //值传递
int main() {
struct Money money;
fill(&money);
show(money);
return 0;
}
//void fill(const char* Snames[], double* MoneyArray, const int Seasons) {
void fill(struct Money *money) {
for (int i = 0; i < Seasons; i++) {
cout << "Enter " << Snames[i] << " expenes: ";
cin >> money->MoneyArray[i];
}
}
//void show(const char* Snames[], double* MoneyArray, const int Seasons) {
void show(struct Money money) {
double total = 0;
cout << "\nEXPENSE\n";
for (int i = 0; i < Seasons; i++) {
cout << Snames[i] << " : $" << money.MoneyArray[i] << endl;
total += money.MoneyArray[i];
}
cout << "Total EXPENSE : $ " << total << endl;
}
7.9 动态结构体数组定义 student* ptr_stu = new student[class_size];,结构体数组作为形参传递void display3(const student ps[], int n);;需要特别理解,结构体数组和普通数组是一样的,作为函数形参时,student ps[]和student *ps是等价的,传递的都是数组的首地址。但是对于非结构体数组的普通结构体,结构体名称并不是首地址,如下列案
- 清空动态结构体数组
delete[] ptr_stu; display1(ptr_stu[i]);是值传递,对应函数形参void display1(student st);,display2(&ptr_stu[i]);传递的是地址,&是取地址运算符对应的函数形参是void display2(const student *ps);
void display1(student st);
void display2(const student *ps);
for (int i = 0; i < entered; i++) {
display1(ptr_stu[i]);
display2(&ptr_stu[i]);
}
char定义的数组来装字符串,输入时用cin.getline(temp_fullname, SLEN);来接收输入,string类型定义的字符串输入getline(cin, dessert);
string dessert;
getline(cin, dessert);
strlen用于判断char类型数组定义的字符串的长度- 输入数字之后,如果要继续输入新的字符串,需要在数字输入语句后添加
cin.get();
cout << "输入第" << counter+1 << "学生的 ooplevel: ";
cin >> pa[counter].ooplevel;
cin.get();

#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
const int SLEN = 128;
struct student {
char fullname[SLEN];
char hobby[SLEN];
int ooplevel;
};
int getinfo(student *pa, int n);
void display1(student st);
void display2(const student *ps);
void display3(const student ps[], int n);
int main(){
cout << "Enter class size:";
int class_size;
cin >> class_size;
while (cin.get() != '\n')
{
continue;
}
student* ptr_stu = new student[class_size];
int entered = getinfo(ptr_stu, class_size);
cout << " entered = " << entered << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < entered; i++) {
display1(ptr_stu[i]);
display2(&ptr_stu[i]);
}
display3(ptr_stu, entered);
delete[] ptr_stu;
cout << "Done\n";
return 0;
}
void display3(const student ps[], int n)
{
cout << " -----display3(const student ps[], int n) ------- " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << ps[i].fullname << ", hobby is " << ps[i].hobby << " , level is " << ps[i].ooplevel << endl;
}
}
void display2(const student* ps) {
cout << " -----display2(const student* ps) ------- " << endl;
cout << ps->fullname << ", hobby is " << ps->hobby << " , level is " << ps->ooplevel << endl;
}
void display1(student st) {
cout << " -----display1(student st) ------- " << endl;
cout << st.fullname << ", hobby is " << st.hobby << " , level is " << st.ooplevel << endl;
}
int getinfo(student* pa, int n) {
int counter = 0;
char temp_fullname[SLEN], temp_hobby[SLEN];
bool is_blank = false;
while (counter < n && !is_blank)
{
cout << "请输入姓名:";
cin.getline(temp_fullname, SLEN);
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(temp_fullname); i++) {
if (isspace(temp_fullname[i])) {
is_blank = true;
break;
}
}
if (!is_blank) {
cout << "请输入爱好:";
cin.getline(temp_hobby, SLEN);
cout << "输入第" << counter+1 << "学生的 ooplevel: ";
cin >> pa[counter].ooplevel;
cin.get();
strcpy_s(pa[counter].fullname, strlen(temp_fullname)+1, temp_fullname);
strcpy_s(pa[counter].hobby, strlen(temp_hobby)+ 1, temp_hobby);
//cout << pa[counter].fullname << ", hobby is " << pa[counter].hobby << " , level is " << pa[counter].ooplevel << endl;
counter++;
}
}
return counter;
}
7.10 指针数组,多个函数的地址存储在一个数组里面,函数形参是数组,数组里的变量指向不同函数。函数别名,类型定义常用于需要将函数作为参数传递的场景,typedef double (*TPfun) (double x, double y); 定义了一个名为 TPfun 的类型别名,它是一个函数指针类型,指向一个接受两个 double 类型参数(x 和 y)并返回 double 类型值的函数。
TPfun funArray[] = { add,sub };创建了一个指针数组,类型为TPfun,里面存放了两个指针

#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
//定义了一个名为 TPfun 的类型别名,它是一个函数指针类型,
//指向一个接受两个 double 类型参数(x 和 y)并返回 double 类型值的函数。
typedef double (*TPfun) (double x, double y);
double add(double x, double y) {
cout << "加法操作结果:" ;
return x + y;
}
double sub(double x, double y)
{
cout << "减法操作结果:";
return (x - y);
}
void calculate(double x, double y, TPfun funArray[], int fun_num) {
for (int i = 0; i < fun_num; i++) {
cout << funArray[i](x, y) << endl;
}
}
int main(){
TPfun funArray[] = { add,sub };
double x, y;
cout << "输入x y :";
while (cin >> x >> y)
{
calculate(x, y, funArray, sizeof(funArray) / sizeof(funArray[0]));
cout << "输入x y :";
}
return 0;
}
第九章



9.1 普通结构体数组定义golf golfArray[peopleNum];和动态结构体数组定义 golf* golfArray = new golf[peopleNum];,结构体引用作为函数参数传递void setgolf(golf& g, const char* name, int hc);函数声明和实现可以分别放在.h和。cpp文件里面,和放在mian函数里面是一样的,注意和类实现的区分
- 知识点1:结构体数组本很和数组性质一样,结构体数组名就是结构体的地址
- 知识点2:char类型定义的数组,
char name[Len];作为函数形参时,和const char* name是等价的,判断char类型数组的长度和数据拷贝strcpy_s以及strlen,语句strcpy_s(g.fullname, strlen(name) + 1, name);实现char类型数组的数据拷贝 - 知识点3:
cin.getline(name, Len);char类型数组输入 main函数
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <array>
#include "string"
#include <fstream>
#include "golf.h"
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main(){
const int peopleNum = 3;
//golf golfArray[peopleNum]; //普通结构体数组
golf* golfArray = new golf[peopleNum]; //动态结构体数组
for (int i = 0; i < peopleNum; i++) {
int kk = setgolf(golfArray[i]);
if (kk == 0) {
break;
}
showgolf(golfArray[i]);
}
delete[] golfArray;
return 0;
}
golf.h
#pragma once
const int Len = 40;
struct golf {
char fullname[Len];
int handicap;
};
void setgolf(golf &g , const char *name, int hc);
int setgolf(golf& g);
void handicap(golf& g, int hc);
void showgolf(const golf &g);
golf.cpp
#include "golf.h"
#include "string"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//输入信息
void setgolf(golf& g, const char* name, int hc)
{
strcpy_s(g.fullname, strlen(name) + 1, name);
g.handicap = hc;
}
int setgolf(golf& g)
{
char name[Len];
int hc;
cout << "输入名字:";
cin.getline(name, Len);
if (name[0] == '\0') {
return 0;
}
cout << "输入handicap:";
cin >> hc;
cin.get();
setgolf(g, name, hc);
return 1;
}
void handicap(golf& g, int hc)
{
g.handicap = hc;
}
void showgolf(const golf& g)
{
cout << g.fullname << ", handcap is " << g.handicap << endl;
}
9.2.1 static int total = 0;即使在函数里面定义的局部静态变量,也能控制整个函数的累加;void stecount(const char* str)实现char类型的字符串的计数;cin.get(input, Arsize);和cin.getline(input, Arsize);用法一样,都是实现char数组字符串的输入

const int Arsize = 10;
void stecount(const char* str);
int main(){
char input[Arsize];
char next;
cout << "Enter a line:\n";
cin.get(input, Arsize);
while (cin) {
cin.get(next);
while (next != '\n') {
cin.get(next);
}
stecount(input);
cout << "Enter next line(enpty line to quit):\n";
cin.get(input, Arsize);
}
cout << "Byb\n";
return 0;
}
void stecount(const char* str) {
static int total = 0;
int count = 0;
cout << "\" " << str << "\" contains ";
while (*str++)
count++;
total += count;
cout << count << " characters\n";
cout << total << " characters total\n";
}
9.2.2 string字符串和char数组字符串输入接收,前者getline(cin, input);,后者cin.get(input, Arsize);,获取string字符串的长度string.size(); 判断输入是否为空,string字符串直接input != ""。而char字符串char next; cin.get(next); next != '\n'或者取input[0] != '\n'
const int Arsize = 10;
void stecount(string str);
int main(){
string input;
cout << "Enter a line:\n";
getline(cin, input);
while (input != "") {
stecount(input);
cout << "Enter next line(enpty line to quit):\n";
getline(cin, input);
}
cout << "Byb\n";
return 0;
}
void stecount(string str) {
static int total = 0;
int count = str.size();
cout << "\" " << str << "\" contains ";
total += count;
cout << count << " characters\n";
cout << total << " characters total\n";
}
9.3 定位new运算
struct Chaff {
char dross[20];
int slag;
};
char g_buffer[1024];
int main(){
//Chaff* chaff = new Chaff[2];
Chaff* pChaff = new (g_buffer) Chaff[2];
strcpy_s(pChaff[0].dross,strlen("foo")+1, "foo");
pChaff[0].slag = 2;
strcpy_s(pChaff[1].dross, strlen("bar") + 1, "bar");
pChaff[1].slag = 8;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
cout << pChaff[i].dross << '\t' << pChaff[i].slag << endl;
}
delete[] pChaff;
return 0;
}
9.4 普通结构体,作为函数形参时,指针传递,引用传递,直接传递的区别。 namespace SALES定义作用域,调用时,相应的对象需要using namespace SALES;,这样后续就不需要对每个函数调用声明作用域了
通过引用传递,直接操作 s,s 就是 sale2 的别名
void setSales(Sales& s) {}
setSales(sale2); //
通过引用传递,形参用const修饰,因此不允许修改变量
void showSales(const Sales& s) {};
showSales(sale2);
和下列定义等价的,下列定义,即使函数内修改了变量,主函数内的值是不会变了
void showSales(Sales s);
showSales(sale2);
通过指针传递,需要通过指针访问成员,如 s->average
void setSales(Sales* s) {}
setSales(&sale2); //

main
using namespace std;
using namespace SALES;
int main(){
Sales sale1, sale2;
double arr[] = {6,3, 3, 4};
setSales(sale1, arr, QUARTERS);
showSales(sale1);
showSales(sale1);
//cout << "打印sale2" << endl;
//setSales(sale2);
//showSales(sale2);
return 0;
}
Sales.h
#pragma once
namespace SALES
{
const int QUARTERS = 4;
struct Sales
{
double sales[QUARTERS];
double average;
double max;
double min;
};
// copies the lesser of 4 or n items from the array ar
// to the sales member of s and computes and stores the
// average, maximum, and minimum values of the entered items;
// remaining elements of sales, if any, set to 0
void setSales(Sales& s, const double ar[], int n);
// gathers sales for 4 quarters interactively, stores them
// in the sales member of s and computes and stores the
// average, maximum, and minimum values
void setSales(Sales& s);
// display all information in structure s
void showSales(const Sales& s);
static double getMin(const double ar[]);
static double getMax(const double ar[]);
static double getAverage(const double ar[]);
}
Sales.cpp
#include "Sales.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void SALES::setSales(Sales& s, const double ar[], int n)
{
s.average = getAverage(ar);
s.min = getMin(ar);
s.max = getMax(ar);
for (unsigned i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
s.sales[i] = ar[i];
}
}
void SALES::setSales(Sales& s)
{
cout << "输入 " << QUARTERS << "个销售记录" << endl;
double sales;
int counter = 0;
double array[QUARTERS] = {0};
while (counter < QUARTERS) {
cout << "输入" << counter + 1 << "次销售记录";
cin >> array[counter];
s.sales[counter] = array[counter];
counter++;
}
s.average = getAverage(array);
s.min = getMin(array);
s.max = getMax(array);
}
void SALES::showSales(const Sales& s)
{
cout << "s.average = " << s.average <<
", s.max =" << s.max <<
", s.min =" << s.min << endl;
cout << "s.sales: ";
for (int i = 0; i < QUARTERS; i++) {
cout << s.sales[i] << " ";
}
}
double SALES::getMin(const double ar[])
{
double min = ar[0];
for (int i = 1; i < QUARTERS; i++) {
if (min > ar[i]) {
min = ar[i];
}
}
return min;
}
double SALES::getMax(const double ar[])
{
double max = ar[0];
for (int i = 1; i < QUARTERS; i++) {
if (max < ar[i]) {
max = ar[i];
}
}
return max;
}
double SALES::getAverage(const double ar[])
{
double aver = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < QUARTERS; i++) {
aver += ar[i];
}
return aver/QUARTERS;
}
